2022-08-22 来源 : VIP说

前言


抗肿瘤特性

凋亡活性
触发肿瘤细胞凋亡已经被作为一种治疗癌症的有效方法,淫羊藿可诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,淫羊藿70%乙醇提取物可激活结肠癌细胞线粒体依赖性凋亡通路[13]。这为进一步研究从该草药分离的生物活性成分诱导凋亡的活性提供了依据。通常,Icaritin及其他衍生物的凋亡作用与细胞凋亡的内在途径激活有关。Icaritin的治疗可导致多种癌细胞(肝癌[14, 15]、AML[16]、淋巴瘤[17, 18]、子宫内膜癌[19]、CML[20]、)中Bax/Bcl2比值的增加、细胞色素c的释放、多聚(ADP-核糖)聚合酶的裂解和半胱天冬酶的活化,这些可被各种信号通路调控[14],如表1所示。

表1. Icaritin的凋亡活性

图1. Icaritin通过抑制JAK/STAT3 signaling、MAPK/ERK signaling、EGFR signaling等多种机制发挥凋亡作用。
细胞周期调控

图2. Icaritin对细胞周期的调节作用

表2. Icaritin对细胞周期的调控
血管生成抑制

表3. Icaritin的抗血管生成作用

侵袭和转移抑制
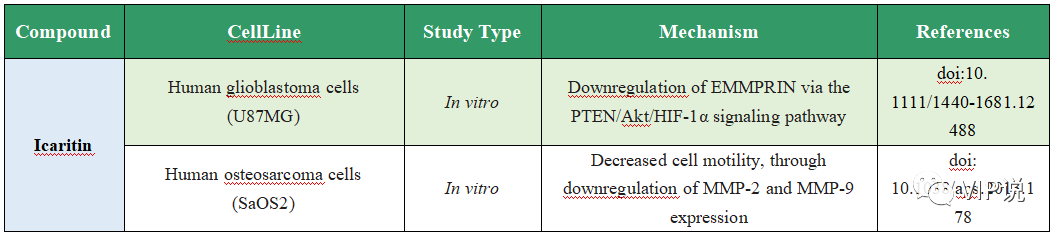
表4. Icaritin的抗肿瘤转移作用

图4. Icaritin的抗肿瘤转移作用
抑制激素依赖型肿瘤
抑制耐药肿瘤细胞
免疫调节

总 结


图5. Icaritin的抗肿瘤完整机制

参考文献:
1. Ma H, He X, Yang Y, Li M, Hao D, Jia Z. The genus Epimedium: an ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review. J Ethnopharmacol 2011; 134(3):519-541.
2. Arief ZM, Munshi AH, Shawl AS. Evaluation of medicinal value of Epimedium elatum on the basis of pharmacologically active constituents, Icariin and Icariside-II. Pak J Pharm Sci 2015; 28(5):1665-1669.
3. Liu J, Ye H, Lou Y. Determination of rat urinary metabolites of icariin in vivo and estrogenic activities of its metabolites on MCF-7 cells. Pharmazie 2005; 60(2):120-125.
4. Xu W, Zhang Y, Yang M, Shen Z, Zhang X, Zhang W, et al. LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of icariin and its major metabolites in rat plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2007; 45(4):667-672.
5. Yao D, Xie XH, Wang XL, Wan C, Lee YW, Chen SH, et al. Icaritin, an exogenous phytomolecule, enhances osteogenesis but not angiogenesis--an in vitro efficacy study. PLoS One 2012; 7(8):e41264.
6. Wang Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Qi L, Lou Y. Neuroprotective effects of icaritin against beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat neuronal cells via estrogen-dependent pathway. Neuroscience 2007; 145(3):911-922.
7. A SWL, B GCA, C GPHL, A SCWL, A MPMH, A LW, et al. Icaritin protects against oxidative stress-induced injury in cardiac H9c2 cells via Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 and calcium signalling pathways. Journal of Functional Foods 2015; 18:213-223.
8. Geng YD, Yang L, Zhang C, Kong LY. Blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway by Icariside II results in reduced cell proliferation of osteosarcoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 2014; 73:7-16.
9. Lee KS, Lee HJ, Ahn KS, Kim SH, Nam D, Kim DK, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2/prostaglandin E2 pathway mediates icariside II induced apoptosis in human PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett 2009; 280(1):93-100.
10. Zheng Q, Liu WW, Li B, Chen HJ, Zhu WS, Yang GX, et al. Anticancer effect of icaritin on human lung cancer cells through inducing S phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 2014; 34(4):497-503.
11. Wang Y, Dong H, Zhu M, Ou Y, Zhang J, Luo H, et al. Icariin exterts negative effects on human gastric cancer cell invasion and migration by vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein via Rac1 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 2010; 635(1-3):40-48.
12. Li S, Priceman SJ, Xin H, Zhang W, Deng J, Liu Y, et al. Icaritin inhibits JAK/STAT3 signaling and growth of renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One 2013; 8(12):e81657.
13. Kwon TE, Duksung Womens University, Seoul. Effect of Epimedium koreanum Nakai on Apoptosis in HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells. Food Engineering Progress 2014.
14. He J, Wang Y, Duan F, Jiang H, Chen MF, Tang SY. Icaritin induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells via the JNK1 signaling pathway independent of the estrogen receptor. Planta Med 2010; 76(16):1834-1839.
15. Sun L, Peng Q, Qu L, Gong L, Si J. Anticancer agent icaritin induces apoptosis through caspase-dependent pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep 2015; 11(4):3094-3100.
16. Li Q, Huai L, Zhang C, Wang C, Jia Y, Chen Y, et al. Icaritin induces AML cell apoptosis via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signal pathways. Int J Hematol 2013; 97(5):617-623.
17. Li ZJ, Yao C, Liu SF, Chen L, Xi YM, Zhang W, et al. Cytotoxic effect of icaritin and its mechanisms in inducing apoptosis in human burkitt lymphoma cell line. Biomed Res Int 2014; 2014:391512.
18. Wu T, Wang S, Wu J, Lin Z, Sui X, Xu X, et al. Icaritin induces lytic cytotoxicity in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2015; 34:17.
19. Tong JS, Zhang QH, Huang X, Fu XQ, Qi ST, Wang YP, et al. Icaritin causes sustained ERK1/2 activation and induces apoptosis in human endometrial cancer cells. PLoS One 2011; 6(3):e16781.
20. Zhu J, Li Z, Zhang G, Meng K, Kuang W, Li J, et al. Icaritin shows potent anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3 /AKT signalings. PLoS One 2011; 6(8):e23720.
21. Huang X, Zhu D, Lou Y. A novel anticancer agent, icaritin, induced cell growth inhibition, G1 arrest and mitochondrial transmembrane potential drop in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2007; 564(1-3):26-36.
22. Guo Y, Zhang X, Meng J, Wang ZY. An anticancer agent icaritin induces sustained activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and inhibits growth of breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2011; 658(2-3):114-122.
23. Zhu S, Wang Z, Li Z, Peng H, Luo Y, Deng M, et al. Icaritin suppresses multiple myeloma, by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3. Oncotarget 2015; 6(12):10460-10472.
24. Orr BA, Eberhart CG. Molecular pathways: not a simple tube--the many functions of blood vessels. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21(1):18-23.
25. Yu X, Tong Y, Han XQ, Kwok HF, Yue GG, Lau CB, et al. Anti-angiogenic activity of Herba Epimedii on zebrafish embryos in vivo and HUVECs in vitro. Phytother Res 2013; 27(9):1368-1375.
26. Da Z. Suppressive Effect of Icaritin on Angiogenesis and Its Mechanisms. Journal of International Translational Medicine 2014.
27. Hong J, Zhang Z, Lv W, Zhang M, Chen C, Yang S, et al. Icaritin synergistically enhances the radiosensitivity of 4T1 breast cancer cells. PLoS One 2013; 8(8):e71347.
28. Fares J, Fares MY, Khachfe HH, Salhab HA, Fares Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: a hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020; 5(1):28.
29. Xu B, Jiang C, Han H, Liu H, Tang M, Liu L, et al. Icaritin inhibits the invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of glioblastoma cells by targeting EMMPRIN via PTEN/AKt/HIF-1alpha signalling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2015; 42(12):1296-1307.
30. Rau KM, Kang HY, Cha TL, Miller SA, Hung MC. The mechanisms and managements of hormone-therapy resistance in breast and prostate cancers. Endocr Relat Cancer 2005; 12(3):511-532.
31. Tiong CT, Chen C, Zhang SJ, Li J, Soshilov A, Denison MS, et al. A novel prenylflavone restricts breast cancer cell growth through AhR-mediated destabilization of ERalpha protein. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33(5):1089-1097.
32. Sun F, Indran IR, Zhang ZW, Tan MH, Li Y, Lim ZL, et al. A novel prostate cancer therapeutic strategy using icaritin-activated arylhydrocarbon-receptor to co-target androgen receptor and its splice variants. Carcinogenesis 2015; 36(7):757-768.
33. Vinogradov S, Wei X. Cancer stem cells and drug resistance: the potential of nanomedicine. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2012; 7(4):597-615.
34. Zhao H, Guo Y, Li S, Han R, Ying J, Zhu H, et al. A novel anti-cancer agent Icaritin suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma initiation and malignant growth through the IL-6/Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Oncotarget 2015; 6(31):31927-31943.
35. Sun L, Chen W, Qu L, Wu J, Si J. Icaritin reverses multidrug resistance of HepG2/ADR human hepatoma cells via downregulation of MDR1 and Pglycoprotein expression. Mol Med Rep 2013; 8(6):1883-1887.
36. Han H, Xu B, Hou P, Jiang C, Liu L, Tang M, et al. Icaritin Sensitizes Human Glioblastoma Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis. Cell Biochem Biophys 2015; 72(2):533-542.
37. Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9(3):162-174.
38. Marvel D, Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment: expect the unexpected. J Clin Invest 2015; 125(9):3356-3364.
39. Zhou J, Wu J, Chen X, Fortenbery N, Eksioglu E, Kodumudi KN, et al. Icariin and its derivative, ICT, exert anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor effects, and modulate myeloid derived suppressive cells (MDSCs) functions. Int Immunopharmacol 2011; 11(7):890-898.
版权声明:本网站所有注明来源“医微客”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于医微客所有,非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源:”医微客”。本网所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源和作者,转载仅作观点分享,版权归原作者所有。不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。 本站拥有对此声明的最终解释权。





发表评论
注册或登后即可发表评论
登录注册
全部评论(0)