2023-10-16





针对我国阿尔茨海默病的统计调查显示,截至2021年,中国60岁及以上人群中,轻度认知障碍的老年人群占比达到15.54%,痴呆症患病率为6.04%,其中阿尔茨海默病为3.94%,血管性痴呆为1.57%,其他类型痴呆为0.53%,作为最常见的认知障碍疾病,全球现存的阿尔茨海默病及其他痴呆患病人数达5100多万例,其中我国患病人数约占全球数量的25.5%。根据首都医科大学宣武医院贾建平教授团队在《柳叶刀》神经病学子刊发表的文章显示,我国每年在阿尔茨海默病上支出的费用高达1677亿美元,预计到2030年增加约2倍,到2050年可能会升至10倍,达到1.89万亿美元8。更进一步的了解阿尔茨海默病发生发展的原因,开发针对阿尔茨海默病的新疗法新药物在日趋老龄化社会的当下迫在眉睫。
参考文献:
1. Mathys, Hansruedi et al. “Single-cell atlas reveals correlates of high cognitive function, dementia, and resilience to Alzheimer's disease pathology.” Cell vol. 186,20 (2023): 4365-4385.e27. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.039
2. Blanchard JW, et al. APOE4 impairs myelination via cholesterol dysregulation in oligodendrocytes. Nature. 2022. Epub Nov. 16. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05439-w.
3. Xiong, Xushen et al. “Epigenomic dissection of Alzheimer's disease pinpoints causal variants and reveals epigenome erosion.” Cell vol. 186,20 (2023): 4422-4437.e21. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.040
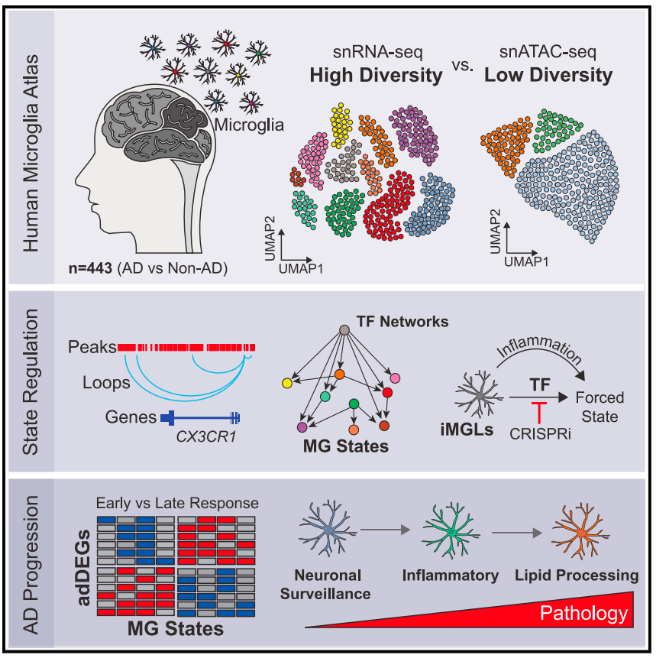
4. Sun, Na et al. “Human microglial state dynamics in Alzheimer's disease progression.” Cell vol. 186,20 (2023): 4386-4403.e29. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.037
5. Gjoneska, Elizabeta et al. “Conserved epigenomic signals in mice and humans reveal immune basis of Alzheimer's disease.” Nature vol. 518,7539 (2015): 365-9. doi:10.1038/nature14252
6. Durak O, Gao F, Tsai L-H. Chd8 mediates cortical neurogenesis through transcriptional regulation of cell cycle and Wnt signaling genes. Nat Neurosci. 2016 Oct 3. Doi: 10/10138/nn.4400. [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 27694995.
7. Dileep, Vishnu et al. “Neuronal DNA double-strand breaks lead to genome structural variations and 3D genome disruption in neurodegeneration.” Cell vol. 186,20 (2023): 4404-4421.e20. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.038
8. Jia, Longfei et al. “Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study.” The Lancet. Public health vol. 5,12 (2020): e661-e671. doi:10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30185-7
百度浏览 来源 : 生物谷
版权声明:本网站所有注明来源“医微客”的文字、图片和音视频资料,版权均属于医微客所有,非经授权,任何媒体、网站或个人不得转载,授权转载时须注明来源:”医微客”。本网所有转载文章系出于传递更多信息之目的,且明确注明来源和作者,转载仅作观点分享,版权归原作者所有。不希望被转载的媒体或个人可与我们联系,我们将立即进行删除处理。 本站拥有对此声明的最终解释权。




发表评论
注册或登后即可发表评论
登录注册
全部评论(0)